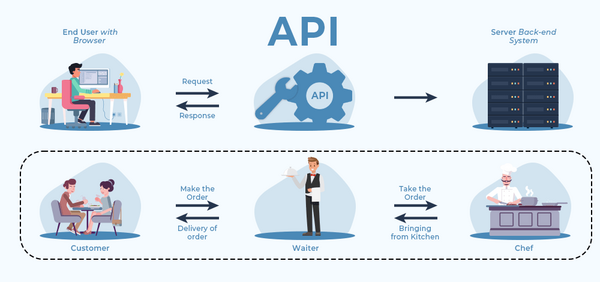
What is APIs?
API is basically a set of functions and procedures which allow one application to access the feature of other application REST is a set of rules or guidelines to build a web API. It is basically an architectural style for networked applications on the web which is limited to client-server based applications. APIs also allow developers to add features and functionality to software by utilizing a rich array of other developers’ APIs. Much of today’s enterprise, mobile and web software depends on a wide range of APIs.
How many Types of APIs?
APIs are extensively accepted and used in web applications. There are four different types of APIs commonly used in web services: public, partner, private and composite. In this context, the API “type” indicates the intended scope of use.
Public APIs. A public API is open and available for use by any outside developer or business. An enterprise that cultivates a business strategy that involves sharing its applications and data with other businesses will develop and offer a public API.
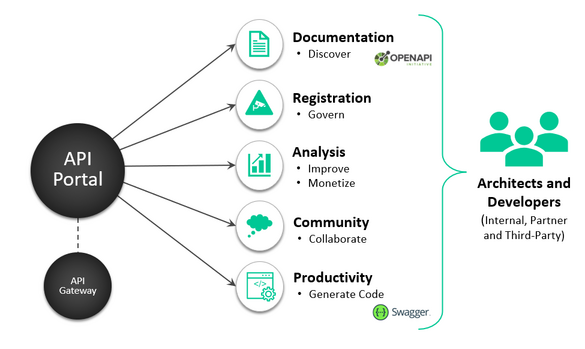
Partner APIs. A partner API, only available to specifically selected and authorized outside developers or API consumers, is a means to facilitate business-to-business activities. For example, if a business wants to selectively share its customer data with outside CRM firms, a partner API can connect the internal customer data system with those external parties — no other API use is permitted.
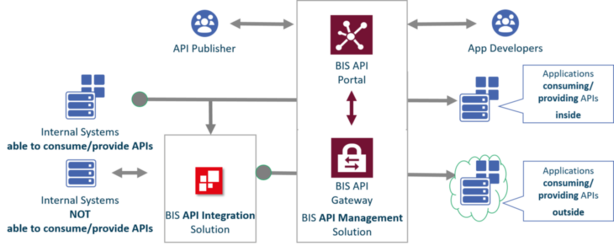
Internal APIs. An internal or private API is intended only for use within the enterprise to connect systems and data within the business.
Composite APIs. Composite APIs generally combine two or more APIs to craft a sequence of related or interdependent operations. Composite APIs can be beneficial to address complex or tightly related API behaviors and can sometimes improve speed and performance over individual APIs.